How does an engine valve function?
We can liken the engine to the heart of an automobile. Then, we can say that an engine valve is a component that acts like a valve inside a heart.
Those heart valves open when the blood needs to start flowing and close later to prevent backflow.
The engine compresses and combusts a mixture of air and fuel in the combustion chamber to convert it into motive energy, and it discharges the combustion gases produced during the process into the atmosphere.
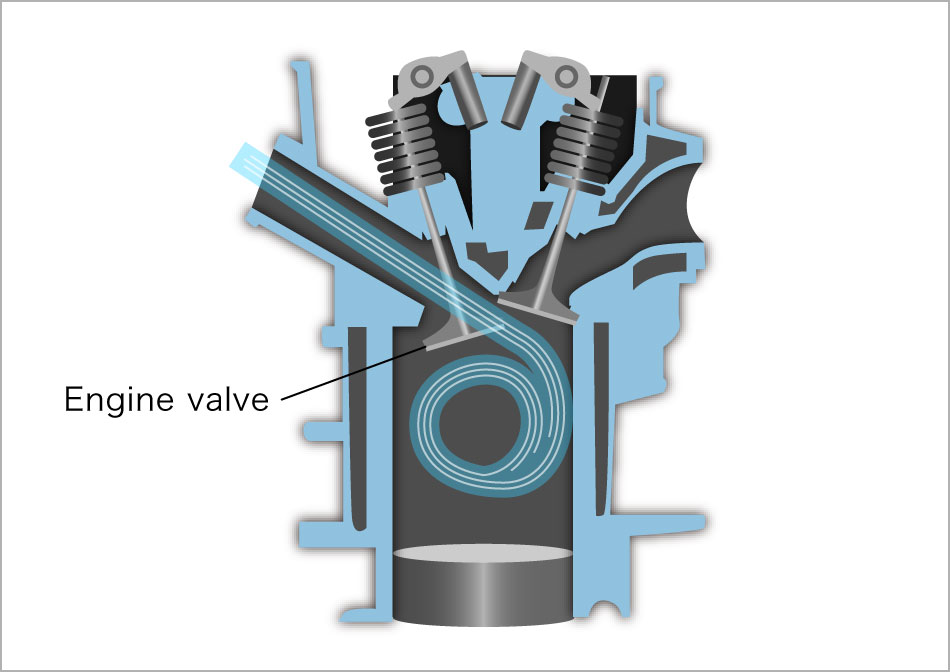
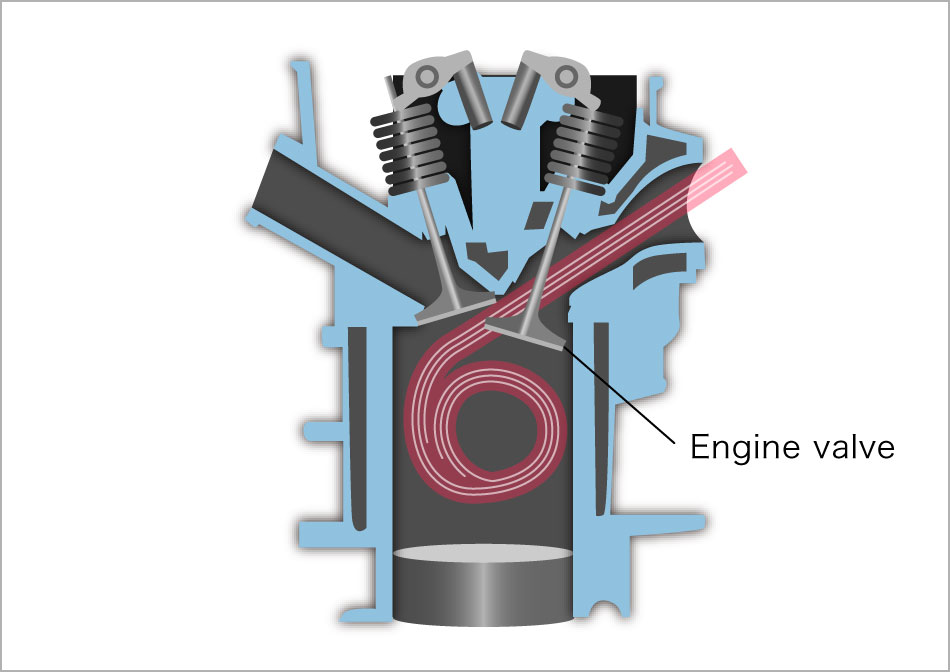
Engine valves are installed at the intake and exhaust ports of the combustion chamber and -- like valves in the heart -- they open and close regularly to control the inflow of a mixture of air and fuel and the discharge of exhaust gases.
What kinds of demands are placed on engine valves?
Engine valves are used in extremely harsh environments that contain some especially noteworthy factors. They are used in very high temperatures, so they are required to have enough strength to withstand heat in the range of 800 to 1000℃. Engine valves also need to move very quickly in their opening and closing operations. For example, if a car is running at 100 km/h, they open and close 1,000 to 1,250 times per minute. During this opening and closing process, the valve and guide rub against each other violently and at high speed. When the valve closes, there is an impact force between the valve seat and the valve, and tensile stress on the valve itself. Engine valves must be able to withstand this severe environment and maintain the performance required for accurate opening and closing.
Added to all this, improved automobile fuel economy is also being demanded. It is well understood that, to achieve better fuel economy, it is best to maintain a ratio of air to fuel that maximizes combustion. but this method also results in extremely high temperatures. This means that engine valves are now required to perform even better under even more challenging conditions.
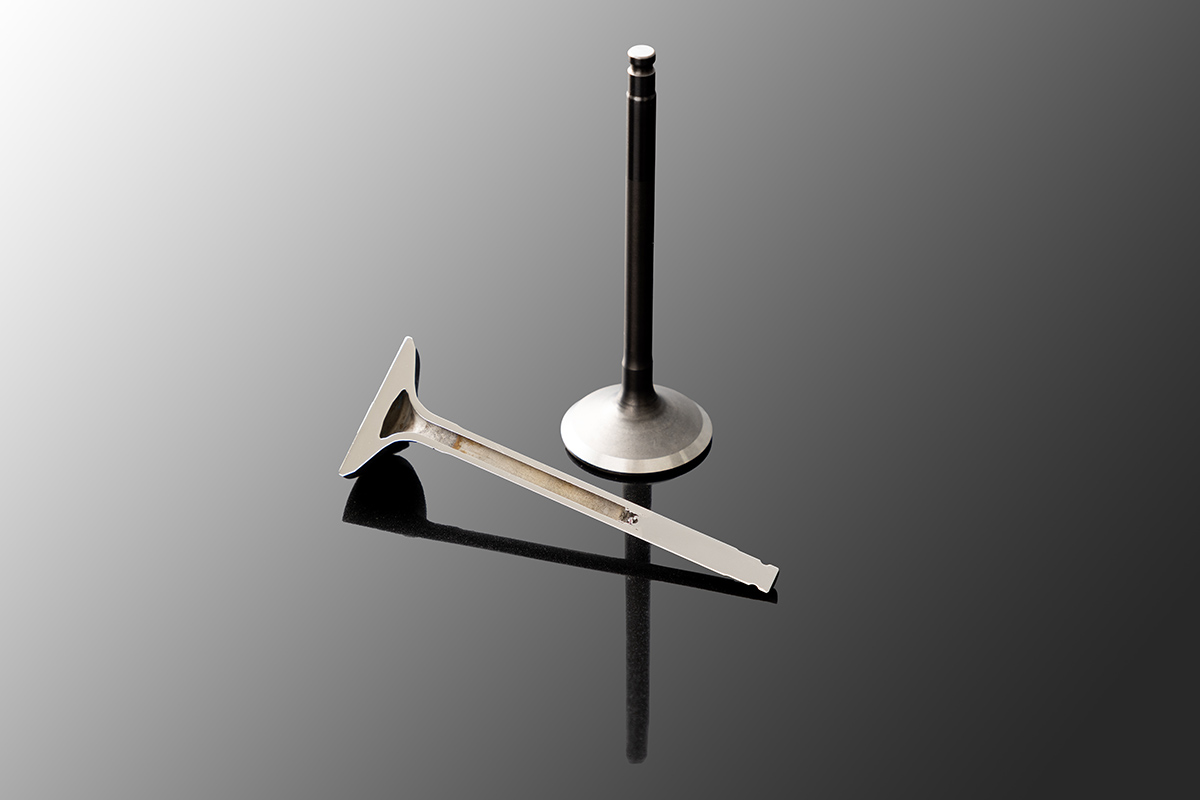

How are engine valves manufactured?
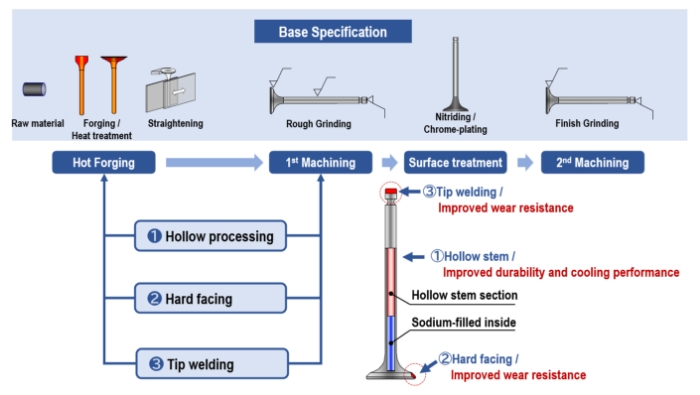
Engine valves are generally manufactured by hot forging, starting with a billet or workpiece cut from steel bar. Hot forging is a technique in which metal is heated to a high temperature and pressed into a mold. After being formed to this shape, the workpiece is then ground to the specified dimensions using a grinder. Areas of the valve subject to great friction and impact are surface-treated or welded using especially strong materials to increase their durability, and areas requiring greater precision are finished and polished. Engine valves must be strong even at high temperatures, so special heat-resistant steel is used. It contains more elements that add strength, such as chromium and nickel, than ordinary steel does. These additions make it more difficult to change the metal’s shape, and both forging and polishing become high-tech processes.
Here's what's great about FUJI OOZX engine valves
1High-quality steel is available to us
Engine valves need to be made of metal that is very durable and heat-resistant. Therefore,“specialty steel” is generally used to manufacture engine valves, and the high cost of this kind of steel is a bottleneck. However, FUJI OOZX is a group company of Daido Steel, one of the major specialty steel manufacturers in Japan. This makes it easy for us to obtain high-quality steel material, and through joint projects with Daido Steel we are in a position to develop new materials to meet the evolution of engines, into the future.
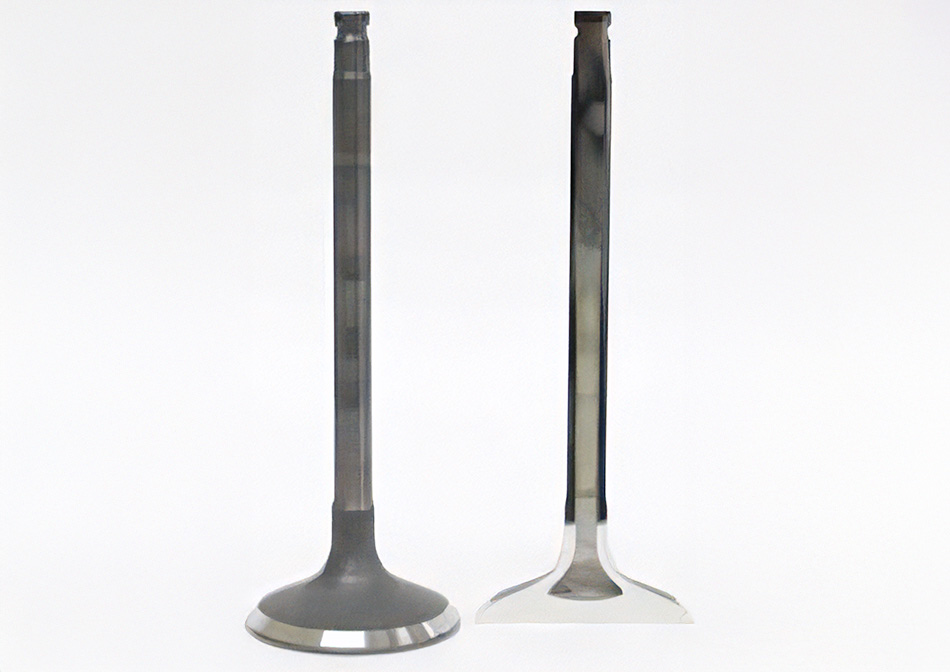


2A full complement of “just-right” production equipment
FUJI OOZX designs its own production equipment to meet various requirements for complicated processing and high productivity. As explained earlier, engine valves are made of very strong specialty steel, which requires high-level forging and polishing techniques. In order to perform these processes successfully, we select the grinding stones, dies, etc.carefully and develop -- on our own -- the production equipment that has the functions we need to ensure high quality as well as improved productivity.

3We use our technological capabilities to solve customers’ needs
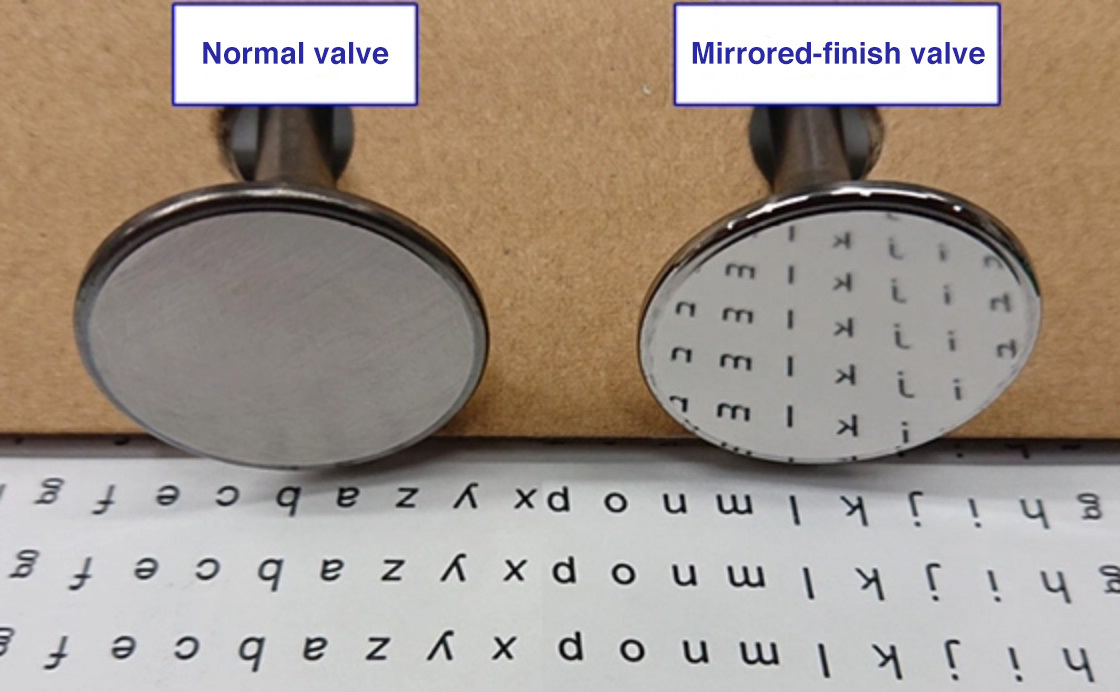
Engine designs keep changing, to provide better and better performance, so we keep working on various technological developments to help make this designed performance a reality. The development of hollow valves is one result of these endeavors. As the combustion temperature of an engine increases, the engine valves approach a level of heat that they cannot withstand. This shortens their service lives. The hollow-stem valve is a typical hollow valve whose stem portion is filled with sodium (acting as a coolant) to facilitate cooling during operation, thereby improving valve durability. In addition, we are now working on the development of a new mirror-finish technique. In this process, the surface of the valve that is exposed to the combustion chamber -- i.e., the combustion surface -- is polished to a mirror-like finish. This reduces the surface area of the combustion face on a microscopic level, and so results in less heat transfer and improved heat flow. When we have production up and running, we are sure our new mirror-finish technique will be contributing to improved combustion efficiency by maintaining lower temperatures inside the combustion chamber. We are thus making two technological contributions to the future of automobiles: enhancing the durability of the engine valves themselves and improving engine efficiency by delivering the high-quality engine valves that help them run better.